Waktunya Menganggap Serius Kim Jong Un dan Ancaman Nuklirnya – Ketika Barat mencemaskan kemungkinan Vladimir Putin beralih ke senjata nuklir di Ukraina, ada risiko bahwa ancaman serupa yang ditimbulkan oleh pemimpin pria lain tidak dianggap serius—seperti ancaman Kim Jong Un dari Korea Utara.
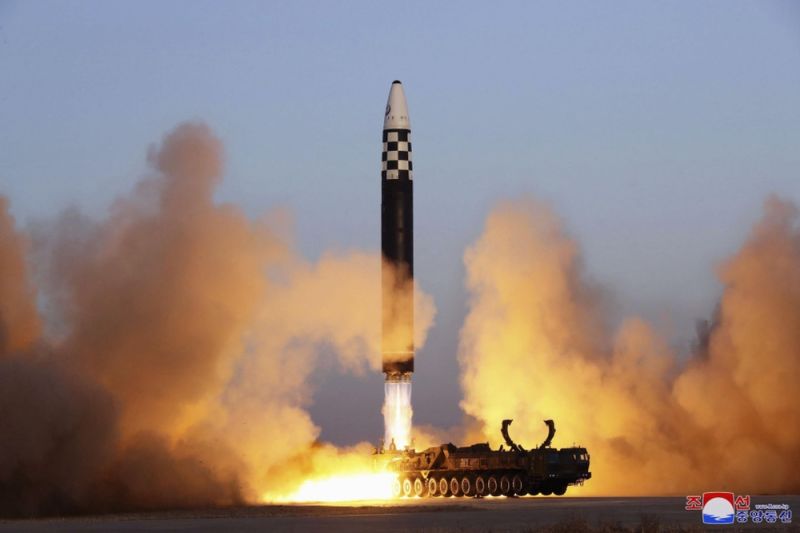
Negara Asia Timur yang terisolasi itu telah melakukan tujuh ledakan rudal berkemampuan nuklir selama 15 hari, dari 25 September hingga 9 Oktober 2022. Satu terbang di atas Jepang , terjun ke Pasifik setelah terbang sejauh 2.800 mil – jarak yang menempatkan Pangkalan militer AS di Guam dalam jangkauan. judi online
Kemudian, pada 10 Oktober – peringatan 77 tahun berdirinya Partai Buruh komunis Korea Utara – media pemerintah mengumumkan bahwa Kim secara pribadi telah melakukan bimbingan lapangan untuk “unit operasi nuklir taktis” negaranya, yang menunjukkan kemampuan untuk “memukul dan memusnahkan target musuh. https://www.lemonaidcars.com/
Benar, persenjataan nuklir Rusia yang sangat besar membuat ancamannya lebih kredibel daripada ancaman Korea Utara. Moskwa memiliki sarana untuk melakukannya, dan ketakutan akan kekalahan di Ukraina dapat menjadi alasan.
Ada alasan lain mengapa ancaman nuklir Kim terdengar kurang menyenangkan, jika tidak sepenuhnya hampa. Pemimpin Korea Utara menyerang banyak orang di Barat hampir sebagai sosok yang menggelikan – seorang diktator narsis, bergizi baik, bagi banyak orang, terlihat lucu.
Ya, dia menyimpan ambisi bom nuklir yang mengkhawatirkan dan memimpin negara putus asa menghadapi kelaparan yang meluas. Tetapi ancamannya yang sesekali untuk menghancurkan tetangganya di selatan – Korea Selatan – disambut oleh banyak orang yang tidak lebih dari sekadar permusuhan badut.
Ambil, misalnya, pidato Presiden Donald Trump tahun 2017 di Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa di mana dia meremehkan Kim sebagai “Manusia Roket dalam misi bunuh diri”.
Tetapi sebagai seorang sarjana sejarah Korea yang telah menyaksikan rezim Korea Utara mengancam akan mengacaukan kawasan, saya yakin Kim harus ditanggapi dengan serius. Dia sangat serius menyelesaikan misi kakek dan ayahnya untuk penyatuan kembali semenanjung Korea. Itu adalah “tugas nasional tertinggi” dinasti, dan tidak banyak yang menunjukkan bahwa Kim tidak akan melakukan apa pun untuk mewujudkannya.
Pendahuluan Serangan Nuklir
Pada tahun 2022 saja, Korea Utara telah menembakkan lebih dari 30 rudal, termasuk enam proyektil balistik antarbenua. Kegiatan ini merupakan “pelanggaran terbuka terhadap sanksi Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa,” seperti yang dilaporkan Panel Pakar PBB tentang Korea Utara pada bulan September.
Namun, belum ada satu pun Resolusi Dewan Keamanan Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa yang baru disahkan sebagai tanggapan atas pelanggaran berantai ini. Dan saya ragu ada yang akan datang bahkan setelah uji coba nuklir besar, yang akan segera terjadi.
Anggota Dewan Keamanan Rusia dan China, yang mendukung sanksi PBB sebelumnya setelah rudal dan uji coba nuklir Korea Utara, tidak mungkin melakukannya lagi kali ini di tengah keretakan geopolitik yang berkembang dengan Barat. Kedua negara secara aktif memblokir langkah-langkah yang dipimpin oleh AS pada awal tahun ini.
Lebih buruk lagi, pernyataan baru-baru ini oleh Putin dan Kim telah mengembalikan gagasan yang dulunya tidak terpikirkan tentang sebuah negara yang terlebih dahulu menyerang negara tetangga.
Pada bulan September, Korea Utara mengumumkan “undang-undang tentang kebijakan negara tentang kekuatan nuklir” baru. Ini menetapkan kondisi di mana Korea Utara akan menggunakan senjata nuklir.
Dalam istilah yang luas dan samar-samar, undang-undang tersebut mengutip “mengambil alih dalam perang” dan “mau tidak mau terpaksa dan tidak bisa tidak menggunakan senjata nuklir” sebagai alasan untuk menggunakan senjata pamungkas.
Dalam menguraikan pendekatan aksi nuklir yang cukup terbuka, Kim telah meningkatkan retorika dan berusaha menormalkan hak untuk menyerang lebih dulu.
Ini meletakkan dasar untuk menggunakan setiap gerakan “bermusuhan” oleh Korea Selatan – yang didefinisikan oleh rezim secara luas sebagai apa pun antara kritik atas pelanggaran hak asasi manusia hingga latihan militer pertahanan gabungan dengan Amerika Serikat – sebagai dalih untuk serangan nuklir pendahuluan.
Kim tampaknya berargumen bahwa itu adalah haknya untuk menggunakan senjata nuklir kapan pun dia menganggap perlu. Ini adalah prospek yang benar-benar menakutkan.
Sebuah Siklus Eskalasi
Peluncuran rudal berkemampuan nuklir baru-baru ini, yang datang hanya beberapa minggu setelah doktrin nuklir baru dan bertepatan dengan eskalasi Putin di Ukraina, tampaknya memojokkan AS dan memanfaatkan perpecahan Perang Dingin yang sedang berkembang. Kim menempa norma baru dalam politik kawasan.
Mungkin sulit untuk menerima bahwa Korea Utara – aktor ekonomi kecil dibandingkan dengan AS, China, Rusia, Jepang, dan Korea Selatan – telah mengungguli lawan bicaranya yang lebih besar. Namun, selama 30 tahun terakhir diplomasi nuklir, Korea Utaralah yang paling banyak mengambil keputusan – mulai dari mengusulkan pembicaraan, penetapan agenda, dan pengalihan agenda hingga memutuskan kapan harus pergi.
Dalam prosesnya, Pyongyang telah merebut uang tunai, makanan, bahan bakar, dan barang lain senilai miliaran dolar AS dari negara lain sambil membangun sekitar 50 bom nuklir, ICBM, dan senjata strategis lainnya.
Dari pemerintahan Bill Clinton dan George W. Bush saja, Korea Utara menerima bantuan senilai lebih dari US$1,3 miliar sebagai imbalan atas janji palsu denuklirisasi yang berulang kali.
Strategi Korea Utara selama ini adalah strategi yang menggabungkan provokasi yang diperhitungkan, eskalasi bertahap, dan taktik perdamaian pasca-provokasi. Tetapi permainan akhir bagi Kim, seperti ayah dan kakeknya sebelumnya, tetap sama: menang atas Korea Selatan dan menggabungkan rakyat dan wilayahnya di bawah yurisdiksi Korea Utara.
Untuk mengaktifkan ini, Korea Utara perlu mengulangi siklus provokasi dan deeskalasinya sambil terus mengembangkan persenjataan militernya hingga menjadi ancaman nuklir yang jelas dan nyata di daratan AS dan tanggung jawab regional yang tak tertahankan.
Pada saat itu, begitulah strategi berjalan, itu dapat mendorong AS untuk menarik pasukan di Korea Selatan, membuat Korea Selatan rentan untuk tunduk pada rencana Korea Utara.
Strategi Besar Kim
Reunifikasi di bawah persyaratan Korea Utara merupakan inti dari rencana Kim. Dengan demikian, pengamat internasional mungkin bijaksana untuk lebih fokus pada tujuan provokasi Kim, daripada penyebabnya.
Merenungkan “Apa yang menyebabkan Kim menguji nuklir?” dapat membawa beberapa orang ke dalam perangkap yang sama dengan bertanya, “Apa yang menyebabkan Putin menginvasi Ukraina?”
Kedua pertanyaan menganggap agresor lebih reaktif daripada proaktif dan mengabaikan niat muluknya.
Kim Jong Un memiliki strategi besar. Selama Korea Selatan ada sebagai negara Korea yang lebih kaya dan sah secara demokratis yang berfungsi sebagai magnet bagi rakyatnya sendiri, momok model reunifikasi Jerman – di mana Jerman yang lebih kaya menyerap yang lebih miskin – membayangi Kim. Dan itu, dia tidak bisa mengizinkan.
Karena itu, para pemimpin dunia harus berhati-hati: Ketika tiran narsis membuat ancaman nuklir, mereka membawa makna yang mengancam – bahkan ketika diucapkan oleh para lalim yang tampak aneh.